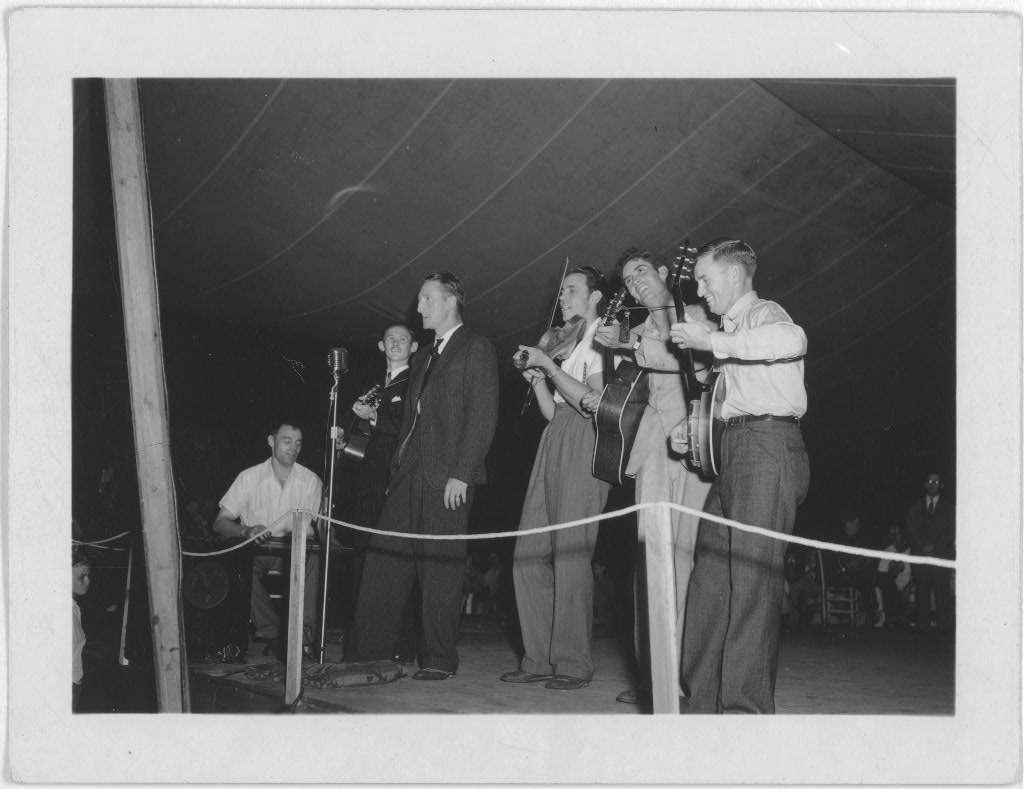
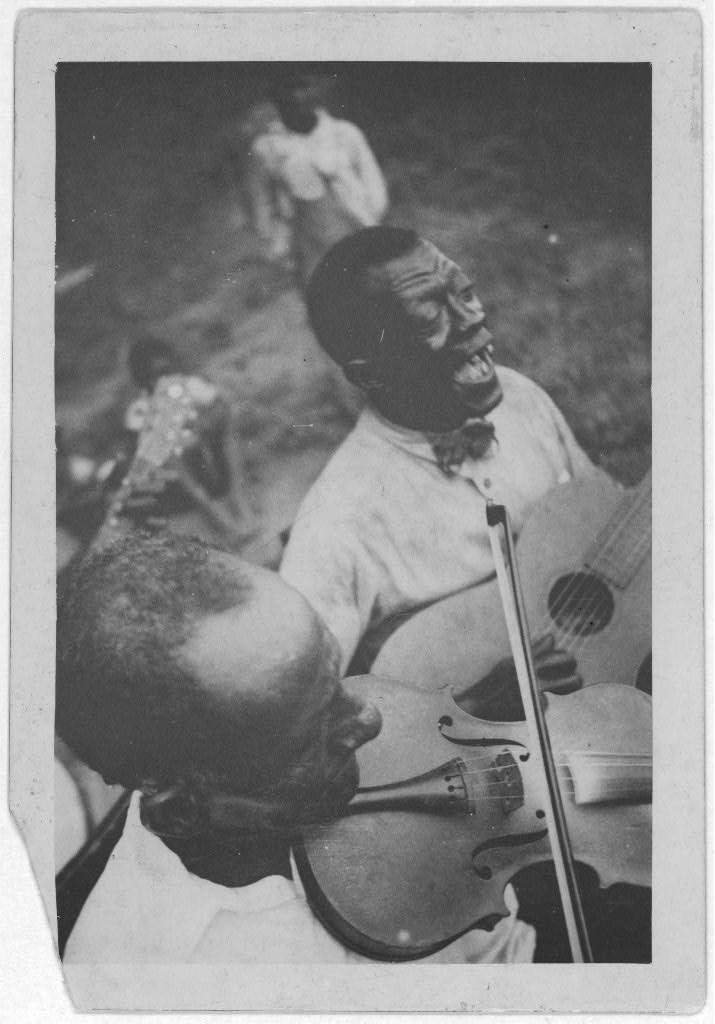
Railroad songs were a genre created by laborers for the railroads in America. The origin of the genre is disputed and rather mysterious. We can all recall “I’ve been Working on the Railroad” (pre Civil War), but it is unclear if that is one example of the genres earliest pieces. Archie Green suggests in “Railroad Songs and Ballads: From the Archive of Folk Song” that “[the songs] welled directly out of the experiences of workers and were composed literally to the rhythm of the handcar. Others were born in Tin Pan Alley rooms or bars. But regardless of birthplace, songs moved up and down the main line or were shunted onto isolated spur tracks.”1 John Lomax had recorded many of these railroad songs. Here is an example of one: http://www.loc.gov/item/lomaxbib000326/ 2
These songs were created by workers to entertain and convey stories up and down the rails. The subjects of the songs, that are recorded, range from the erotic, basic railroad construction, and common themes like love and loss. The creators of the railroads songs included African Americans and many immigrant people. Unfortunately there are little to no record of the songs created by immigrants in different languages and today there is no way of rediscovering those songs. These songs created by African Americans and immigrants created a new slang term for these people called “Gandy Dancers”.
In the article “Country Music and the Souls of White Folk” by Erich Nunn, we get a sense of the effect that the Gandy Dancer’s music has had on country music, we are told, “In My Husband, Jimmie Rodgers, a biography of her late husband published in 1935, Carrie Williamson (“Mrs. Jimmie”) Rodgers presents Jimmie as a crucible in which the “darkey songs” he learned as a boy are transmuted by “the natural music in his Irish soul” into something distinctive and new.”3 The songs that Carrie writes on were created by the African American men that worked of the rails and influenced Jimmie Rodgers.
Gandy Dancers used their songs as a method of keeping rhythm for the laborers of the railroad and striking in time amongst the laborers. Here is a short snippet of a documentary done on Gandy Dancers: 4
- Green, Archie. “Railroad Songs and Ballads.” Archive of Folk Song, 1968. Accessed February 26, 2018. https://www.loc.gov/folklife/LP/AFS_L61_opt.pdf.
- Lomax, John A, Ruby T Lomax, and Arthur Bell. John Henry. near Varner, Arkansas, 1939. Audio. Retrieved from the Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/item/lomaxbib000326/. (Accessed February 26, 2018.)
- Nunn, Erich. Country Music and the Souls of White Folk. Wayne State University Press.
- Folkstreamer. “Gandy Dancers.” YouTube. June 23, 2008. Accessed February 26, 2018. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=025QQwTwzdU.