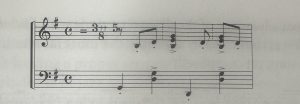Aaron Copland was not just a prolific composer, but also wrote extensively about both his own works and his contemporaries. In a preface to a collection of his writing, he’s described as having “epitomized the ideal of the composer-writer” in his career.1 He also wrote about trends and occurrences in music, particularly American music. One example of this is a short essay from 1927 titled “Jazz Structure and Influence.”
In the essay, Copland aims to contribute to analytical and critical writing about jazz, a field of study which had just begun to emerge. The essay’s general thesis argues that jazz’s main contribution to music as a whole is its rhythmic innovations. He begins by consulting a few different sources for a definition of jazz, including composer Virgil Thomson and music critic Henry O. Osgood’s book, So This Is Jazz. Both of the definitions emphasize rhythm, and the central function of “‘a counterpoint of regular against irregular beats.’”2
Copland continues to build on these assertions by pinpointing a particular type of syncopation that is unique to jazz. He traces the development of this jazz rhythm through spirituals, ragtime, and the foxtrot. He asserts that “Modern jazz began with the fox trot,”3 and identifies a specific rhythmic motif, pictured below. By putting it over four quarter notes, “the play of two independent rhythms…” creates “a molecule of jazz.”4 He clarifies later that polyrhythms themselves were not invented by jazz, but that “the polyrhythms of jazz are different in quality and effect… The peculiar excitement they produce by clashing two definitely and regularly marked rhythms is unprecedented in occidental music.”5
Copland then moves into an analysis of the ways in which this identifying aspect of jazz has “achieved a new synthesis in music.”6 This is also where his rhetoric begins to feel problematic for a modern day reader. Copland posits several times that jazz is “so difficult for ordinary ears” that these polyrhythms only appear a few measures at a time in contemporary music, and goes on to credit Gershwin as having written the “most original jazz song yet composed.”7 These statements indirectly communicate a belief that jazz’s rhythmic complexity places it above music “developed among primitive races.”8 Also, he places a white man at the pinnacle of achievement in a genre that he even describes as having Black (specifically African-American) origins. He provides some nuance when he argues that European composers have “exploited it as an exotic novelty.”9 However, his concluding statements describing jazz as “indigenous, music an American has heard as a child,” and encouraging American composers to draw on it as a musical resource, are ignorant of the actual Indigenous music of the Americas, as well as the institutional racism in America that complicates the use of jazz by white composers as inspiration and source material.10
1 Kostelanetz, Richard. “Preface.” In Aaron Copland: A Reader : Selected Writings 1923-1972, by Aaron Copland. New York: Routledge, 2004.