https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0pu3ByHBeU0
“So police think they have the authority to kill a minority.” -Ice Cube
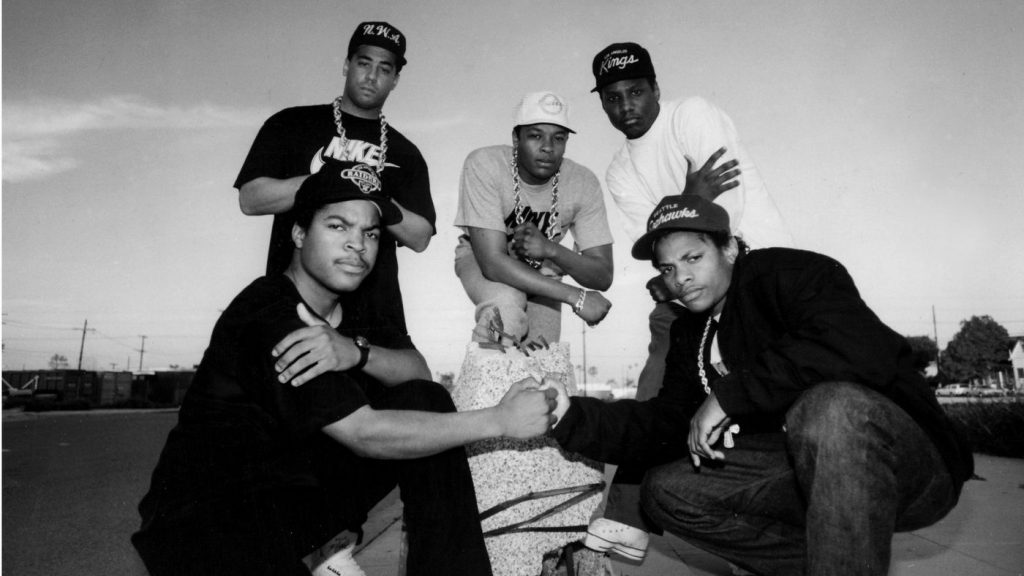
In 1988, the famous rap group called NWA received a letter written by Milt Ahlerich, assistant director of the FBI office of public affairs. The letter enveloped the idea that NWA was advocating for violence against local police officers. Later, NWA clarified that their music was not advocating for action, rather reflecting on their personal experiences with police brutality. This letter was perceived by many as a means of artistic censorship, which caused much controversy across the nation. Many people felt that their amendment of free speech was being threatened by the FBI. According to Ahlerich, he felt that he was representing the sentiment of all the police departments across the nation, stating, “I believe my views reflect the opinion of the entire law enforcement community.” Ahlerich was specifically referring to the censorship of the song, “Fuck The Police” which was written by rapper Ice Cube from NWA.
The entire incident reflected the oppression of expression at the hand of the government. Whether the claim was racialized or not, the FBI’s decision to write such a letter actually worsened attitudes among minorities because it showed that the government will censor any form of personal expression. It created an “us vs. them” feeling among many people.
Los Angeles Times journalist Steve Hochman writes this particular article from a 3rd person perspective. When you read the article, you get to hear all sides of the story, including the FBI member, Milt Ahlerich. Ultimately, Hochman does end up including an argument that music should not be censored by government entities by utilizing quotes stated by Danny Goldberg, chairman of the Southern California affiliate of the American Civil Liberties Union and a recording industry executive. The article was written in 1989, which gave the writer some time for more information on the incident to arise, since the letter was sent to Priority Records, the label that represented NWA, in August 1988.
Although this source highlights the overall story from all angles of the issue, there are more articles that may highlight or focus on the controversy that immediately followed the publication of the FBI letter to NWA. This incident surely created some heated debates across the United States, and only brought NWA more recognition for their art. Hearing from those sides would be paired well with this primary source.
Sources Cited:
1973eazyme. “N.W.A. vs. the FBI [1989].” YouTube. March 20, 2010. Accessed May 01, 2018. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0pu3ByHBeU0.
Hochman, Steve. “Compton Rappers Versus the Letter of the Law: FBI Claims Song by N.W.A. Advocates Violence on Police.” Los Angeles Times. October 05, 1989. Accessed April 29, 2018. http://articles.latimes.com/1989-10-05/entertainment/ca-1046_1_law-enforcement.