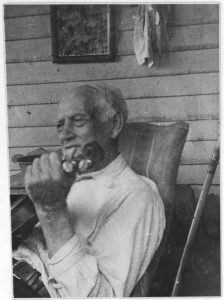As I began looking through images of bluegrass musicians from almost a century ago, I realized that amidst the controversial discussion about which culture bluegrass music sprang from, one element in this polarized history remains constant. It was present whether the musician was Celtic or Cajun, young or old, man or woman.
Front porches… they abound in the bluegrass music world. Scroll through the Lomax photo archives from the 1930s, or do a quick, modern-day Google search, and your results will be similar. Front porches have become a constant, universal symbol of a bluegrass musician. Front porches had no racial bias–they crossed the lines between races at a time when no other thing did. Cajun fiddlers and white fiddlers, black guitarists and Mexican guitarists, cajun singers and black singer-songwriters alike; Lomax images show that front porches were the bluegrass musician’s favorite place.
Nicknamed “pickin’ parlors,”[1] front porches became the unofficial location for jam sessions to break out in 1930s southern communities. One might argue that front porches are a favorite performance venue for bluegrass musicians because of their great acoustics, or because the intense heat of the south required musicians to play outside in the breeze, but I’d like to think it’s deeper than that. I think that by playing on a porch, these musicians were inviting neighbors, relatives, and friends to enjoy this musical tradition.
The front porch lives on in the modern bluegrass scene. There’s a Spotify-curated playlist called Front Porch: Sit back, stay awhile, and savor the soft, sweet sounds of this folksy collection. Front porches remain in country music today. There’s a Front Porch Bluegrass band, an annual Front Porch Bluegrass Festival and Pork Roast, and a bluegrass radio station called Front Porch. It seems that we simply can’t call music “bluegrass” without reference to a front porch.
No matter the person’s race, front porches offered their wooden floors and rocking chairs to any musician.
[1] Patrik Jonsson Correspondent of The Christian,Science Monitor. “Pulled Up by the Banjo Strings: ALL Edition].” The Christian Science Monitor, Jun 23, 2005. https://search.proquest.com/docview/405544729?accountid=351.
Pictures referenced:
Lomax, Alan, photographer. Singers & dancers, New Bight, Cat Island, July. Bahamas Cat Island, 1935. July. Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660223/.
Lomax, Alan, photographer. Pete Steele and family, Hamilton, Ohio. Hamilton Ohio United States, 1938. Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660375/.
Lomax, Ruby T, photographer. Lolo Mendoza and Chico Real, with guitars, at the home of Mrs. Sarah Kleberg Shelton, Kingsville, Texas. Kingsville Texas United States, 1940. [Sept. 20] Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660028/.
Lomax, Alan, photographer. Bill Tatnall, sitting, playing guitar, Frederica, Georgia. Frederica Georgia United States, 1935. June. Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660089/.
Lomax, Ruby T, photographer. Cajun fiddler, Louisiana. Louisiana United States, 1934. Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660087/.
Lomax, Alan, photographer. Wayne Perry playing fiddle, Crowley, Louisiana. Crowley Louisiana United States, None. [Between 1934 and 1950] Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660067/.
Lomax, Alan, photographer. Cajun singers, southwest Louisiana. Louisiana United States, 1934. Summer. Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2007660227/.